Jupyter Notebook vs Kaggle: Installation Guide and Key Differences
Jupyter Notebook vs Kaggle: Installation Guide and Key Differences
When starting a journey in data science, two of the most popular tools you’ll encounter are Jupyter Notebook and Kaggle. Both platforms have their strengths, but they serve different purposes. In this post, we’ll explore their features, installation processes, and key differences. Let’s dive in!
What is Jupyter Notebook?
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. It is widely used in data science for prototyping and interactive data analysis.
Key Features of Jupyter Notebook:
- Supports multiple languages like Python, R, and Julia.
- Interactive code execution with real-time output.
- Easy integration with libraries like Pandas, Matplotlib, and TensorFlow.
- Works offline on your local system.
How to Install Jupyter Notebook:
- Ensure you have Python installed on your system.
- Install Jupyter Notebook using pip:
pip install notebook - Launch the notebook with:
This will open a web interface in your browser, where you can createjupyter notebook.ipynbfiles.
What is Kaggle?
Kaggle is an online platform for data science and machine learning enthusiasts. It offers datasets, competitions, and collaborative tools like notebooks (a cloud-based Jupyter-like environment).
Key Features of Kaggle:
- Access to a vast repository of datasets.
- Free access to GPUs and TPUs for machine learning tasks.
- A collaborative environment where users can share their notebooks and insights.
- A vibrant community and competitive environment to improve your skills.
How to Set Up Kaggle API:
- Install the Kaggle API:
pip install kaggle - Download your API key:
- Go to your Kaggle account settings.
- Click on Create New API Token, and a
kaggle.jsonfile will be downloaded.
- Place the
kaggle.jsonfile in the following location:- Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.kaggle\kaggle.json - Mac/Linux:
~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
- Windows:
You can now use Kaggle’s API to download datasets or submit work to competitions.
Key Differences Between Jupyter Notebook and Kaggle
| Feature | Jupyter Notebook | Kaggle |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Local coding and prototyping | Online collaboration and sharing |
| Setup | Requires local installation | Cloud-based, no setup needed |
| Resources | Uses your local system resources | Free GPU, TPU for ML tasks |
| Data | Must be loaded locally | Easy access to Kaggle datasets |
| Offline Use | Fully offline | It requires an internet connection |
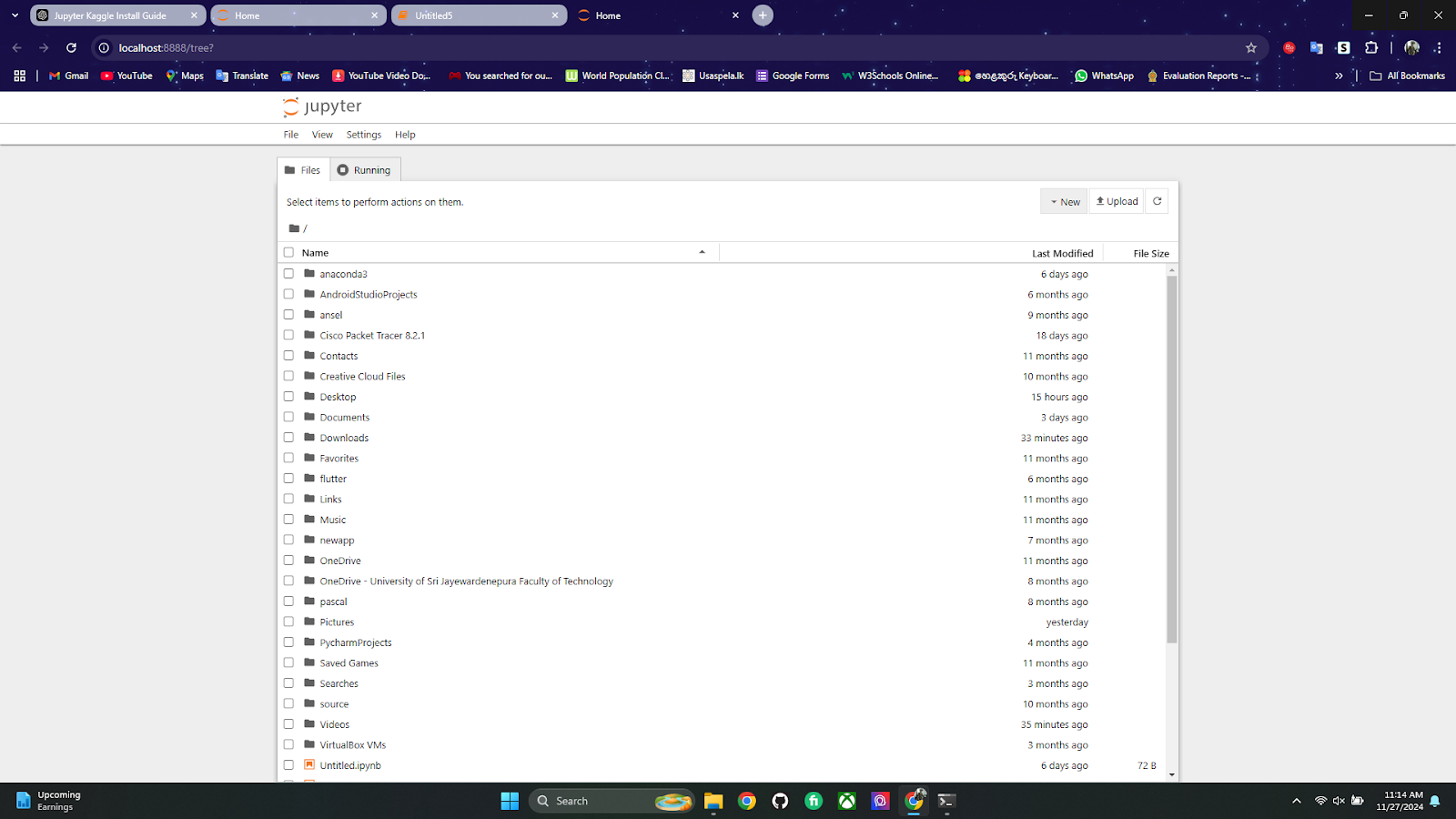
Jupyter Notebook Interface
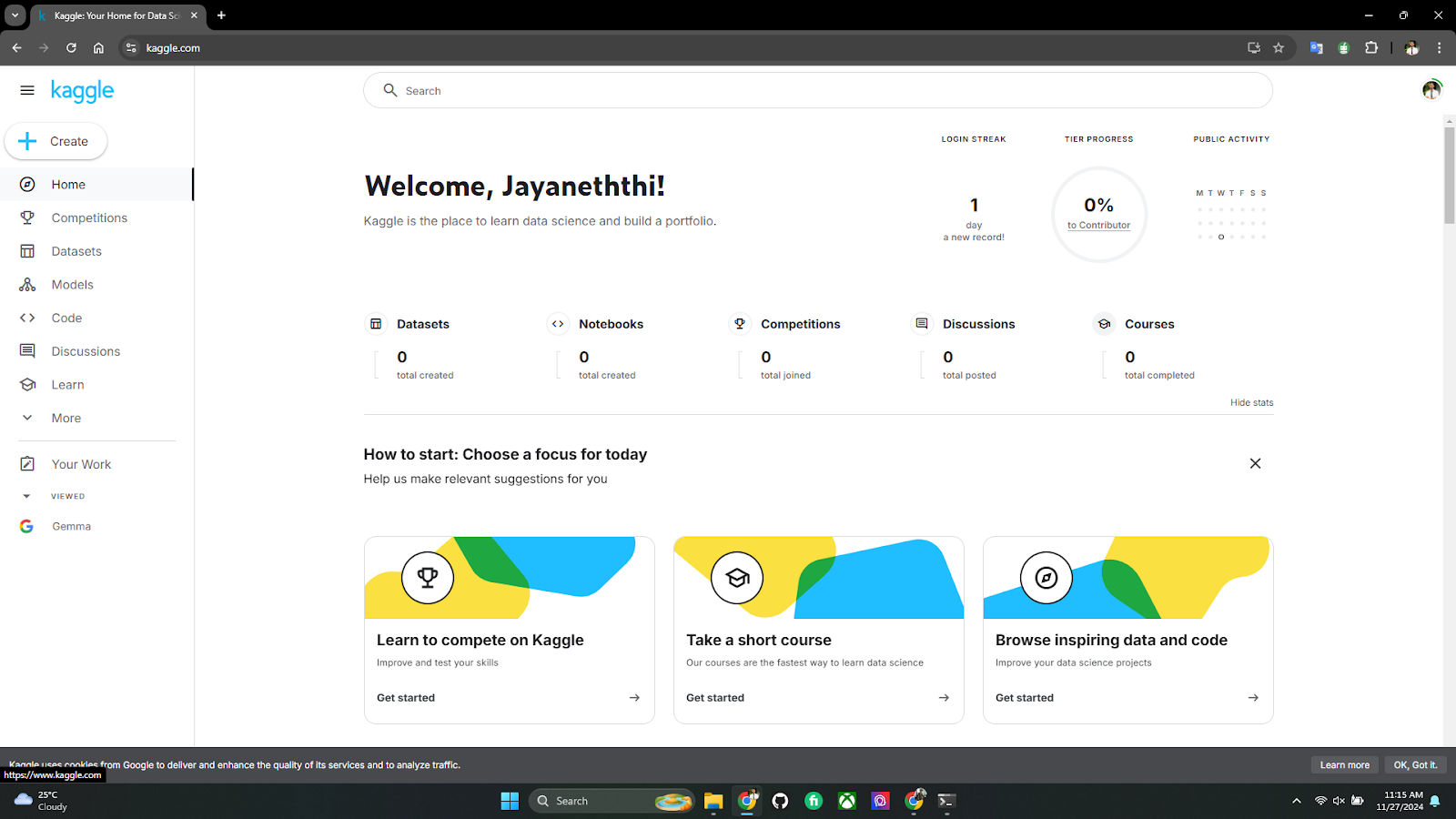
Kaggle Notebook Interface
Kaggle’s Notebook interface is cloud-based and supports Python and R. Here’s an example of Kaggle’s dataset browser:
How to Use Them Together
Both tools can complement each other. For instance:
- Use Jupyter Notebook for detailed experimentation and offline work.
- Use Kaggle to participate in competitions and access high-performance GPUs.
You can also download Kaggle datasets via the API and process them in Jupyter Notebook:
kaggle datasets download -d username/dataset-name
Conclusion
Jupyter Notebook and Kaggle are essential tools for data scientists and machine learning practitioners. While Jupyter Notebook excels in local, interactive coding, Kaggle offers a collaborative, resource-rich cloud environment. Understanding their differences and learning how to use both effectively will elevate your data science journey.





Comments
Post a Comment